HVAC systems are key components of building mechanical systems that offer consumers thermal comfort and good indoor air quality. According to numerous zones, locations, and distribution, HVAC systems can be divided into central and local systems. Heating, ventilation, and cooling or air-conditioning equipment are the three main types of HVAC equipment.

What is a Condenser?
However, Condensers are considered the backbone of any HVAC system. The HVAC system’s condenser unit is critical to maintaining a comfortable home environment. The mechanism’s interior unit gathers heat from your home’s air, while the condenser unit is in charge of expelling that heat to the outside air. The condenser unit, which is located on the outside of the system, aids in the proper heat exchange process.
Since the condenser carries out its functions backstage, it is frequently overlooked during an HVAC system’s maintenance and repair schedules. Some of the importance of a condenser unit is addressed here so that it receives proper attention in the system. However, before looking at what the condenser accomplishes in the system, it’s important to know how it interacts with other processes.
What are the different types of Tubing and Condensers?
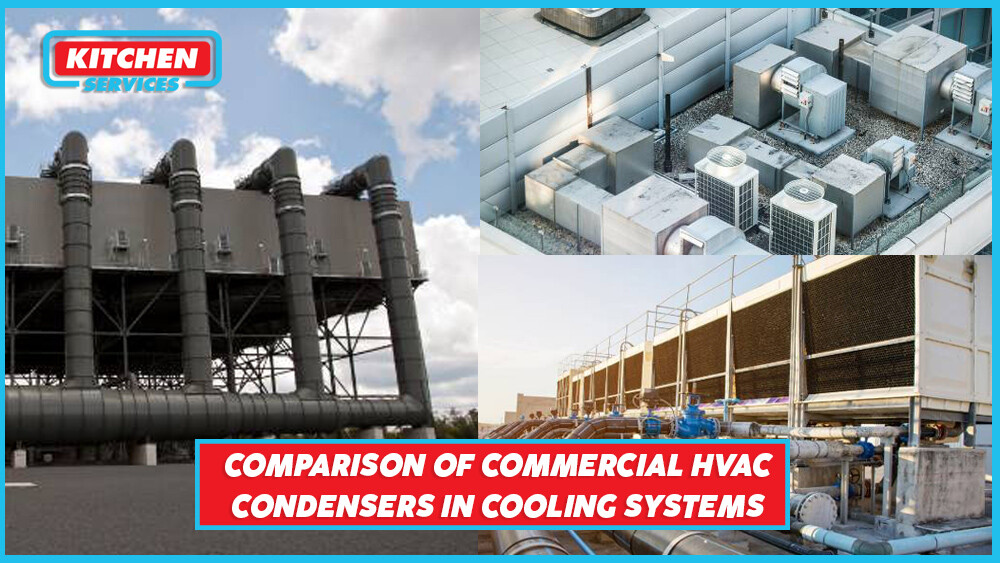
With variations in types and sizes, you will find quite a variety of condensers in the market. The variation is usually caused by the refrigerant tubing or the cooling method for which a condenser is designed. We will compare and contrast the many types of commercial HVAC condensers. However, below we have given you an overview of how tubing can differ from one another.
- Finned Tubes: These tubes are supposed to magnificently increase the surface area.
- Plain Tube: As the name suggests, these are the generic type used for tubing.
- Plate Types: In this type of tubing, many layers of platers are stacked to make a series of channels for the liquid to flow easily.
Series-pass and parallel tubes: These are high-end and complicated types of tubing but also considered the most efficient tubing type.

Types of Condensers in Commercial HVAC System
As mentioned above, condensers in an HVAC system vary from one another on the basis of their cooling methods. There are three different types of cooling methods present in a condenser.
- Air-cooled condensers
- Water-cooled condensers
- Combined air and water-cooled condensers

What is an Air-Cooled Condenser?
Air-cooled condensers have an easy design to understand, a design that relies on ordinary airflow to keep them cold. A fan blows over the condenser coils, causing the refrigerant within the coils to cool as the air passes through. The condensate from the air is collected in a pan below. This design is ideal for smaller HVAC systems and may be used in both small houses and offices.
The benefits of using an air-cooled condenser are many. Some of them are listed below.
- You will no longer have to do manual water piping.
- Saves your water expenses.
- A water disposal system is no longer a necessity.
- The mineral content present in the water does not cause much of a scaling issue in your system.
- The installation of an air-cooled condenser is simpler and the starting cost is also lower.
As far as disadvantages are concerned, let’s shed some light on them as well.
- An air-cooled condenser needs increased power per ton refrigeration.
- It requires frequent maintenance. It must be free of dirt, dander, and lint, at all times as these obstruct airflow, resulting in less air going over the coils and hence less cooling.
- The dirt can badly affect your condenser coils as well.
- Since it has a shorter compressor life, hence, it is not suitable for bigger areas.

What is a Water-Cooled Condenser?
Water-cooled condensers are a more environmentally friendly alternative than air-cooled condensers. Water runs via a network of tubes and sprays onto the condenser coil, which is cooled by the condensers. The gaseous refrigerant cools down here, and the water that has come into contact with the coils evaporates. A water-cooled condenser is sometimes known as a double-pipe condenser because of the two-pipe construction from the water and refrigerant.
If we study the anatomy of a water-cooled condenser, three varieties are regularly used. Shell and tube, shell and coil, and double tube are the three options. The shell and tube form is the most prevalent, and it comes in sizes ranging from two tons to several hundred tons. In comparison to the air-cooled form, this design requires less electricity per ton of refrigeration and the compressors can last longer.
Below we have enlisted some benefits of water-cooled condensers.
- Eco-friendly
- This type has proven to be economical as it does not cause additional water disposal issues.
- It makes less to no noise.
- These are used for large capacity plants.
Now let’s dig deeper into the disadvantages of water-cooled condensers.
- The installation cost of water-cooled condensers is higher.
- Operating this type is not easy.
- They are more exposed to corrosion.
What is a Combined air and water-cooled condenser?
In this type, water is sprayed onto the coils in this sort of condenser to cool the refrigerant within them. The water evaporates as soon as it comes into contact with the coil, causing a temperature reduction within the coil. As a result, the gaseous refrigerant within the coil condenses, cooling it. Cool air enters the condenser from the bottom and blows across the coils in addition to the water.
Both the water and the air work together to return the refrigerant in the coil to a liquid condition. Furthermore, similar to the water-cooled condenser, as the water vapor cools down to a liquid condition, it flows back into the system, spraying the coils once more.
Advantages of Combined Air and Water-Cooled Condenser:
- Budget-friendly as compared to water-cooled condensers.
- Ideal for areas with low water supply.
Disadvantages of Combined Air-Water Cooled Condenser:
- Due to the extra need for water recirculation, this type comes with a complicated design.
- You need to carry out its maintenance frequently to avoid leakages or corrosion.